Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kozai, Naofumi; Onuki, Toshihiko; Komarneni, S.*; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Sakai, Takuro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Sato, Takahiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.513 - 518, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:50.24(Instruments & Instrumentation)This study examined removal of cadmium from solution by two materials with high sorptivity for cadmium: a synthetic mica named Na-4 mica and an apatite. At an initial Cd concentration of 1 10
10 M and a starting pH of 3, the distribution coefficient of Na-4 mica for Cd (8.4
M and a starting pH of 3, the distribution coefficient of Na-4 mica for Cd (8.4 10
10 ml/g) was one order of mgnitude of higher than that of apatite (8.2
ml/g) was one order of mgnitude of higher than that of apatite (8.2 10
10 ml/g). On the other thand, micro-PIXE anaysis for a mixture of equal mass of Na-4 mica and apatite contacted with Cd solution under the same conditions revealed that Cd was selectively taken up by the apatite in the mixture, while Cd was not detected on the Na-4 mica in the mixture. This result by micro-PIXE analysis is not what is expected from the above distribution coefficient values of Na-4 mica and apatite. This result can be explained by irreversibility of the uptake and the difference in kinetics of the uptake by the Na-4 mica and apatite.
ml/g). On the other thand, micro-PIXE anaysis for a mixture of equal mass of Na-4 mica and apatite contacted with Cd solution under the same conditions revealed that Cd was selectively taken up by the apatite in the mixture, while Cd was not detected on the Na-4 mica in the mixture. This result by micro-PIXE analysis is not what is expected from the above distribution coefficient values of Na-4 mica and apatite. This result can be explained by irreversibility of the uptake and the difference in kinetics of the uptake by the Na-4 mica and apatite.
Oikawa, Masakazu*; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro; Okumura, Susumu; Inoue, Hiromitsu*; Masuno, Shinichi*; Umemiya, Shinsuke*; Oshiyama, Yoshifumi*; Taira, Yutaka*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210(1-4), p.54 - 58, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:82.89(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210(1-4), p.308 - 311, 2003/09
A method for detecting the ion hit tracks on the mammalian cultured cells at the irradiation time was established. The cells were attached to the ion track detector CR-39 (100  m thick), then irradiated with 13.0 MeV/u 20Ne or 11.5 MeV/u 40Ar ion beams. Immediately after the irradiation, the cells were refilled with medium, then the CR-39 was etched from the opposite side of the cell with alkaline-ethanol solution at 37
m thick), then irradiated with 13.0 MeV/u 20Ne or 11.5 MeV/u 40Ar ion beams. Immediately after the irradiation, the cells were refilled with medium, then the CR-39 was etched from the opposite side of the cell with alkaline-ethanol solution at 37 C. With the 15 min etching treatment, we obtained the accurate information about the spatial distribution of irradiated ions without significant effect on the cell growth. The continuous observation of the individual cell growth indicated that the growth of ion hit cell was reduced compared with that of non-irradiated one.
C. With the 15 min etching treatment, we obtained the accurate information about the spatial distribution of irradiated ions without significant effect on the cell growth. The continuous observation of the individual cell growth indicated that the growth of ion hit cell was reduced compared with that of non-irradiated one.
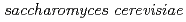
Onuki, Toshihiko; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Kozai, Naofumi; Ozaki, Takuo; Narumi, Issei; Francis, A. J.*; Iefuji, Haruyuki*; Sakai, Takuro; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Sato, Takahiro; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.378 - 382, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.38(Instruments & Instrumentation)We examined the accumulation of Cs and Co, and the presence of other elements in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) cells by the particle induced X-ray emission (PIXE) system, which has low concentration detection limit of ppm, developed at the TIARA facility, JAERI, and by energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) equipped with scanning electron microscope. Addition of 1mM Cs did not have any effect on the growth of the yeast, whereas 0.5 mM Co inhibited its growth. Cells exposed to Cs showed an increase in Cs peak intensity, decrease in P, and no change in Fe, Zn and K with time. In the presence of Co, the intensity of Co and Fe peaks increased with time up to 21 hours while P, K and Zn exhibited no clear trend. These results suggest that PIXE is a useful technique to detect low concentration of elements in microbial cells as well as monitor their changes as function of growth.
Onuki, Toshihiko; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Kozai, Naofumi; Sakai, Takuro; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Sato, Takahiro; Oikawa, Masakazu*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.407 - 411, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:64.66(Instruments & Instrumentation)Sorption behavior of Co by lichen biomass has been studied in the foliose lichen Permotrema tinctorum in solution between pH 3 and 5. Sorption of Co by P. tinctorum reached equilibrium within 24 hours. Co uptake was independent of solution pHs between 3 and 5. Two-dimensional distribution of Co indicates that the sorbed Co is distributed in upper and lower surfaces, and medullary layers at 1 day after contact with P. tinctorum. Highest density in the two-dimensional distribution of Co is obtained in the lower surface suggesting that Co is sorbed by melanin-like pigment contained in the lower surface. Interestingly, the density of Co in algal layer is lower than those in medullary layer. Two-dimensional distribution of Co does not correspond to Fe indicating that Co is not adsorbed on the Fe-containing minerals trapped on P. tinctorum. It is concluded that high accumulation of Co by P. tinctorum is caused by the sorption on not only both surfaces, but medullary layer.
Ishii, Yasuyuki; Isoya, Akira*; Kojima, Takuji
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.70 - 74, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:64.66(Instruments & Instrumentation)The conception for this microbeam formation, which consists in combining beam contraction effect of acceleration process with the lens action, was published in 1991. The test machine was installed in JAERI. The study of reducing beam size showed that the incident beam condition strongly depend on its size. Recently about 40 keV stable microbeam  of 0.1
of 0.1  m order in radius has been obtained after optimizing the ion beam injection system. The test machine is composed of a duoplasmatron-type discharge source, an initial acceleration system, a main acceleration lens system, and microbeam diameter measurement system. We will present the schematic of the test machine and the result of the beam size measurement. Performance of the system will also show to depend mostly on how nicely a low energy injection beam is prepared at the entrance region.
m order in radius has been obtained after optimizing the ion beam injection system. The test machine is composed of a duoplasmatron-type discharge source, an initial acceleration system, a main acceleration lens system, and microbeam diameter measurement system. We will present the schematic of the test machine and the result of the beam size measurement. Performance of the system will also show to depend mostly on how nicely a low energy injection beam is prepared at the entrance region.
Oshima, Takeshi; Lee, K. K.; Onoda, Shinobu*; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Laird, J. S.; Hirao, Toshio; Ito, Hisayoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.201 - 205, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.69(Instruments & Instrumentation)Electrodes on SiC pn diode were studied uising Transient Ion Beam Induced Current system (TIBIC). pn junction of SiC diode was formed by phosphorus ion implantation at 800 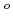 C and subsequent annealing at 1800
C and subsequent annealing at 1800 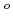 C for 1 min in Ar. Electrodes of diode were fabricated (1) Al evaporation and sintering at 850
C for 1 min in Ar. Electrodes of diode were fabricated (1) Al evaporation and sintering at 850 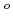 C or (2) one more Al evaporation after the process mentioned above. TIBIC measurement using 15 MeV-O and 12 MeV-Ni ion micro beam. As the result, non-uniformity for transient current from the electrodes of diode (1)was observed. As for diode (2), such non-uniformity was not observed. On the other hand, the value of collected charges was the same for both diodes. This indicates that the quality of pn junction is the almost same for both diodes. For current-voltage characteristics, both diodes showed a order of pA at reverse bias of 30 V and turn-on at forward bias of 2V which are ideal for SiC diode. Thus, we can conclude that we obtain the information on electrical characteristics of electrodes which is not obtained from normal current-voltage measurement.
C or (2) one more Al evaporation after the process mentioned above. TIBIC measurement using 15 MeV-O and 12 MeV-Ni ion micro beam. As the result, non-uniformity for transient current from the electrodes of diode (1)was observed. As for diode (2), such non-uniformity was not observed. On the other hand, the value of collected charges was the same for both diodes. This indicates that the quality of pn junction is the almost same for both diodes. For current-voltage characteristics, both diodes showed a order of pA at reverse bias of 30 V and turn-on at forward bias of 2V which are ideal for SiC diode. Thus, we can conclude that we obtain the information on electrical characteristics of electrodes which is not obtained from normal current-voltage measurement.
Lee, K. K.; Oshima, Takeshi; Saint, A.*; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Jamieson, D. N.*; Ito, Hisayoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.489 - 494, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:78.49(Instruments & Instrumentation)To obtain the information on radiation damage of 6H-SiC devices, ion beam induced charge collection (IBICC) for 6H-SiC schottky diodes irradiated with proton, alpha and carbon micro beam 10 to 10
to 10 ions/cm
ions/cm was studied. No significant difference of degradation was observed between p- and n-substrates irradiated with 2MeV-alpha micro beam. The decrease in IBCC shows a good agreement with the calculation using non ionizing energy loss (NIEL). As a result of ion luminescence and ultra violet photo luminescence, the level of 2.32 eV was observed.
was studied. No significant difference of degradation was observed between p- and n-substrates irradiated with 2MeV-alpha micro beam. The decrease in IBCC shows a good agreement with the calculation using non ionizing energy loss (NIEL). As a result of ion luminescence and ultra violet photo luminescence, the level of 2.32 eV was observed.
Fukuda, Mitsuhiro; Kurashima, Satoshi; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Okumura, Susumu; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Nakamura, Yoshiteru; Nara, Takayuki; Agematsu, Takashi; Ishibori, Ikuo; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.33 - 36, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.69(Instruments & Instrumentation)A heavy ion microbeam with energy of hundreds MeV is a significantly useful probe for research in biotechnology. A single-ion hitting technique using a 260 MeV  Ne
Ne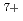 microbeam is being developed at the JAERI AVF cyclotron facility for biofunction elucidation. Production of a microbeam with a spot size of one micro-meter in diameter requires reducing the energy spread of the beam to 0.02 % to minimize an effect of chromatic aberrations in focusing lenses. The typical energy spread of the cyclotron beam is around 0.1 % in an ordinary acceleration mode using a sinusoidal voltage waveform. The energy spread can be reduced by superimposing the fifth-harmonic voltage waveform on the fundamental one to generate a flattop waveform for uniform energy gain. We have designed an additional coaxial cavity to generate the fifth-harmonic voltage, coupled to the main resonator of one-fourth wavelength coaxial type. In a power test we successfully observed the fifth-harmonic voltage waveform by picking up an acceleration voltage signal.
microbeam is being developed at the JAERI AVF cyclotron facility for biofunction elucidation. Production of a microbeam with a spot size of one micro-meter in diameter requires reducing the energy spread of the beam to 0.02 % to minimize an effect of chromatic aberrations in focusing lenses. The typical energy spread of the cyclotron beam is around 0.1 % in an ordinary acceleration mode using a sinusoidal voltage waveform. The energy spread can be reduced by superimposing the fifth-harmonic voltage waveform on the fundamental one to generate a flattop waveform for uniform energy gain. We have designed an additional coaxial cavity to generate the fifth-harmonic voltage, coupled to the main resonator of one-fourth wavelength coaxial type. In a power test we successfully observed the fifth-harmonic voltage waveform by picking up an acceleration voltage signal.
Nishijima, Toshiji*; Hearne, S. M.*; Jamieson, D. N.*; Oshima, Takeshi; Lee, K. K.; Ito, Hisayoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.196 - 200, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.51(Instruments & Instrumentation)The radiation damage in silicon carbide (SiC) schottky diode was studied using ion beam induced current (IBIC). Schottky diodes with electrodes of 30  m on n- or p-type 6H-SiC were fabricated using the evaporation of Al, Ni, and Au. To study the radiation damage of diodes, the 2MeV-He ion micro beam with a diameter of 1
m on n- or p-type 6H-SiC were fabricated using the evaporation of Al, Ni, and Au. To study the radiation damage of diodes, the 2MeV-He ion micro beam with a diameter of 1  m was irradiated from 10
m was irradiated from 10 to 10
to 10 /cm
/cm into a 10
into a 10  m
m  10
10  m area. As the result, the value of IBIC decreased with increasing the dose of 2 MeV-He. This indicates that the charge collection decreases by the recombination centers introduced by irradiation.
m area. As the result, the value of IBIC decreased with increasing the dose of 2 MeV-He. This indicates that the charge collection decreases by the recombination centers introduced by irradiation.
Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Keizo*; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Sakai, Takuro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Arakawa, Kazuo; Matsuyama, Shigeo*; Yamazaki, Hiromichi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.113 - 116, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.51(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new detection apparatus for both low energy X-rays and back-scattered protons of MeV energy and its measurement system were developed. The detection apparatus consists of a multi-element detector, pre-amplifiers with active reset system and so on. The detector elements are arranged in the shape of a pentagonal pyramid and fully cover the sample. On each one detection side, 9 detector elements are arranged. The entire detection system consists thus of 45 detector elements. The micro-beam irradiates the sample through the center of the pentagonal pyramid and X-rays emitted from the sample are detected in close to  geometry. This novel detection setup has about 10 times the sensitivity of a conventional Micro-PIXE camera. The counting rate of back-scattered protons per detection element is small despite lack of a passive absorber. It appears possible that X-rays from the very small quantity of elements could also be detected. The advantage over a conventional Micro-PIXE camera includes simultaneous detection of back-scattered protons from N, C and O.
geometry. This novel detection setup has about 10 times the sensitivity of a conventional Micro-PIXE camera. The counting rate of back-scattered protons per detection element is small despite lack of a passive absorber. It appears possible that X-rays from the very small quantity of elements could also be detected. The advantage over a conventional Micro-PIXE camera includes simultaneous detection of back-scattered protons from N, C and O.
Kamiya, Tomihiro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Oshima, Takeshi; Hirao, Toshio; Lee, K. K.; Onoda, Shinobu*; Laird, J. S.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.206 - 210, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.51(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Hiroshi; Sudo, Yukio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.1 - 5, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.69(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English